Methyl trapping is a situation in which folate becomes trapped and unusable by the body. It is defined as a functional folate deficiency that alters homocysteine metabolism such that folate–dependent resynthesis of methionine is compromised.
Methyl trapping was originally described in Downs Syndrome (trisomy 21) where plasma levels of homocysteine, methionine, S-adenosylhomocysteine and S-adenosylmethionine were all significantly decreased, suggesting a depression in cellular methylation capacity. Elevated transsulfation activity with depletion of glutathione was also observed in Downs Syndrome due to the presence of an additional CBS allele, and up-regulated chromosome 21 SOD SNPs causing oxidative stress.(1)
The term methyl trapping is now applied to the cascade of symptoms of neuroexcitation following supplementation with folate, or B12 or SAMe as a first line treatment for MTHFR SNPs. The unassuming consumer who takes supplements with methylating B vitamins may experience varying degrees of neurotoxic symptoms manifested as apparently unprovoked insomnia, rage, anxiety, brain fog and alcohol intolerance (induced sulfite and aldehyde toxicity), often after experiencing a brief period of improvement from low energy and cognitive impairment.
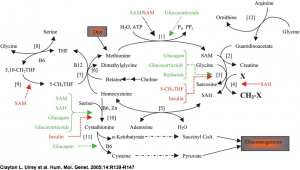 Low energy and irritability occur because of a dysregulation within the methionine cycle due to one-carbon metabolism SNPs causing an accumulation of
Low energy and irritability occur because of a dysregulation within the methionine cycle due to one-carbon metabolism SNPs causing an accumulation of 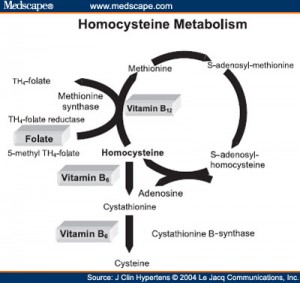 methyl compounds often complicating histamine degradation. A build up of homocysteine is the consequence, often worsened by a bottleneck at CBS (cystathionine beta synthase) due to down-regulating SNPs in the homocysteine clearing transsulfation pathway.
methyl compounds often complicating histamine degradation. A build up of homocysteine is the consequence, often worsened by a bottleneck at CBS (cystathionine beta synthase) due to down-regulating SNPs in the homocysteine clearing transsulfation pathway.
Neuroexcitatory and depression symptoms ensue from the complication of BH2-BH4 pathway reversal, resulting in incomplete ammonia-clearing by the urea cycle and reduced neurotransmitter formation.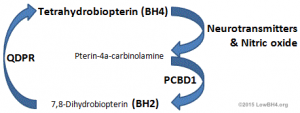
SNPs in MAO and COMT reduce degradation and transporter protein SNPs contribute to dopamine-serotonin imbalance.(2) Patients can also experience poor wound healing, aggravated digestive symptoms of bloating, alternating constipation and diarrhoea, or worsened IBS as a result of reduced methylation capacity.
Clinicians should screen for conditions that may overwhelm transsulfation and detoxification pathways including infection, autoimmunity, toxic body burden, problems with blood sugar and fat metabolism and other inflammatory indications. Non-methylating nutritional support should be provided for mutations in MTR/MTRR, BHMT, SHMT2, MAT1A, CBS, QDPR, OTC, CPS, ARG2, PCBD1, MAOA or B, COMT, HNMT, DHPR, NOS1, 2, 3, SOD1, SOD2, PEMT, PON1, ABCB1, cytochrome P 450 genes and Soluble Carrier Family transporter protein SNPs, ACAT1-02, in deciding when to support Methylation cycle SNPs.
Methyl trapping at a glance:
Practitioners can use cutting-edge cloud-based software curated by naturopathic physicians. Mobocaster is a cutting edge application in Opus23 Pro offering the practitioner scenario-specific genetic analysis including power factors and relevant descriptions.
References:
- Pogribna M, Melnyk S, Pogribny I, Chango A, Yi P, James SJ. Homocysteine
metabolism in children with Down syndrome: in vitro modulation. Am J Hum Genet.
2001 Jul;69(1):88-95. PMID: 11391481. - Finkelstein JD. Pathways and regulation of homocysteine metabolism in mammals.
Semin Thromb Hemost. 2000;26(3):219-25. Review. PMID: 11011839.
